Our Testing Methods
-
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a very high-resolution microscopy technology to study samples at atomic scale.
-
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller Analyzer (BET)
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller analyzer is the most common method for determining the surface area and pore size distribution of powders and porous materials.
-
Cell Counting Kit-8 Assay (CCK-8)
CCK-8 assay allows sensitive colorimetric assays for the determination of cell viability in cell proliferation and cytotoxicity assays.
-
Cell Disruptor
Cell disruptor is used to break down cell walls with high-powered agitation to release biological molecules from inside the cell.
-
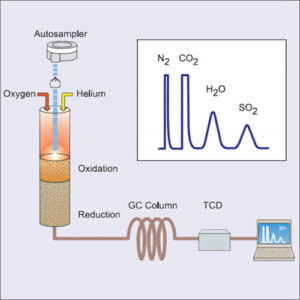
CHNS Analysis
CHNS analyzer can measure the concentrations of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur in petroleum products, biofuels and more.
-
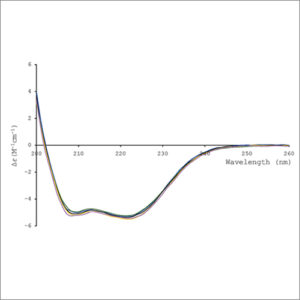
Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy (CD)
Circular dichroism spectroscopy (CD) uses circularly polarized light to investigate structural aspects of optically active chiral media.
-
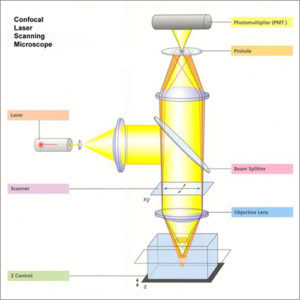
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) is an optical imaging technique to scan an object using a focused laser beam to allow for a 3-D reconstruction.
-
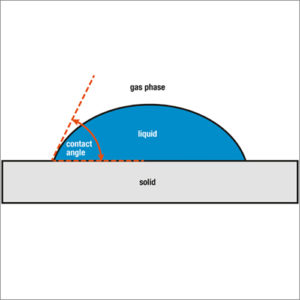
Contact Angle Analysis
Contact angle is an angle where a liquid-vapor interface meets a solid surface. It measures the wettability of a solid by a liquid.
-
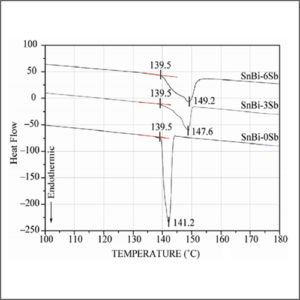
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) is widely used for thermal analysis of materials associated with thermal transitions and chemical reactions.
-
Fluorescence Microscope
Fluorescence microscope uses fluorescence and phosphorescence to study properties of organic or inorganic substances.
-
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Fluorescence spectroscopy measures the fluorescent light emitted from a sample at different wavelengths, after illumination with a xenon flash lamp.
-
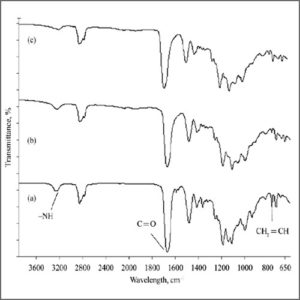
Fourier Transform Infrarred Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is an analytical technique used to identify organic (and in some cases inorganic) materials.
-
Freeze Dryer
Freeze dryer is widely used in dehydration process in order to preserve a perishable material or make the material convenient for transport.
-
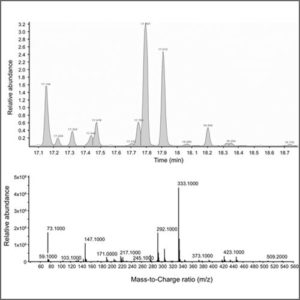
Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Gas chromatography – mass spectrometry (GC-MS) combines the features of gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample.
-
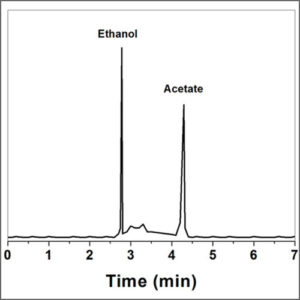
Gas Chromatography with FID/TCD/MS Detectors
Gas chromatography (GC) is used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition.
-
High Performance Liquid Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS)
High performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry.
-
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture.
-
High-Speed Centrifuge
High-speed centrifuge is a method widely used to separate two immiscible substances involving the application of the centripetal force.
-
Inductively Coupled Plasma – Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
ICP-OES is an analytical technique for the detection of trace metals in a sample using the emission spectra from the sample.
-
Inductively Coupled Plasma – Mass Spectrometer (ICP-MS)
ICP-MS is a type of mass spectrometry which is capable of detecting metals and several non-metals at extreme low concentrations.
-
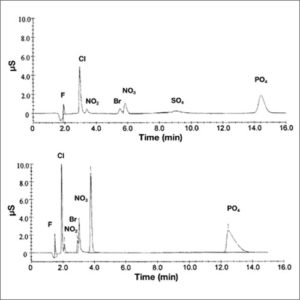
Ion Chromatography (IC)
Ion chromatography is a modified version of HPLC with a capacity for precise and highly sensitive detection of inorganic ions in a complex matrix.
-
Karl Fischer Moisture Titration
Karl Fischer titration is an accurate method to determine trace amounts of water in a sample using uses coulometric or volumetric titration.
-
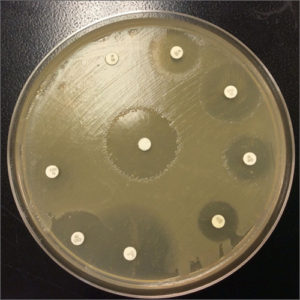
Kirby-Bauer Test (Disk Diffusion Test)
The Kirby-Bauer Test (disk-diffusion test) is a technology to test the effectiveness of antibiotics on a specific micro-organism.
-
Kjeldahl Nitrogen Analyzer
Kjeldahl nitrogen analysis is to quantitatively determine the nitrogen contained in both organic substances and inorganic ammonia and ammonium.
-
Laser Light Scattering (LLS)
Laser light scattering (LLS) is used to determine size of various particles including proteins, polymers, micelles and nanoparticles.
-
Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS)
Mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) is an analytical technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass to charge ratio.
-
Mass Spectrometry (Q-TOF-MS)
Mass spectrometry (Q-TOF-MS) is an analytical technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass to charge ratio.
-
Melt Flow Index Tester
Melt flow index tester is used to measure the melt flow resistance (MFR) of a wide range of thermo-plastic materials in limited interval of time.
-
Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP)
Mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) is used to evaluate porosity, pore size distribution, and pore volume of various solid and powder materials.
-
MTT Assay
MTT assay is used to measure cellular metabolic activity as an indicator of cell viability, proliferation and cytotoxicity.
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
NMR spectroscopy is widely used to confirm the identity of a substance in organic chemistry and often highly predictable for small molecules.
-
Optical Density Measurement (OD600)
Optical density measurement (OD or OD600) is used in microbiology to estimate the concentration of bacteria or other cells in a liquid.
-
Particle Size Analyzer
Particle size analyzer provides accurate, reliable particle size distribution measurements from nanometers to millimetres.
-
Polarimeter
Polarimetry measures the optical rotation angle of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid or solution.
-
Pyridine FTIR Spectroscopy
Pyridine FTIR is a useful method for the quantification ananlysis of the Bronsted and Lewis acidic sites at a catalyst surface.
-
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique used to identify molecules and study chemical bonding and intramolecular bonds.
-
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is commonly used to measure gene expression in real time.
-
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM + EDX)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a non-destructive technique that uses an electron beam probe to analyse surface details down to nano-scale, and to produce high magnification images with high resolution.
-
Shaking Incubator
Shaking incubator is often used for cell culturing, cell aeration, and solubility studies.
-
Size Exclusion Chromatography (GPC/GFC)
Size-exclusion chromatography is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size or by their molecular weight.
-
Thermogravimetric – Differential Thermal Analysis (TGA-DTA)
Thermogravimetric – differential thermal analysis is used to measure the change of physical and chemical properties of materials with high temperature.
-
Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA)
Thermomechanical analysis (TMA) is to study the dimensional change of materials under a constant stress within a temperature regime.
-
Total Organic Carbon Analyzer (TOC)
Total organic carbon analyzer (TOC) is used to determine the amount of carbon found in an organic compound.
-
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Transmission electron microscope (TEM) utilizes energetic electrons to provide morphologic and size information on samples.
-
Universal Testing Machine (UTM)
Universal testing machine (UTM) is used to test the tensile strength, compressive strength and other mechanical properties of materials.
-
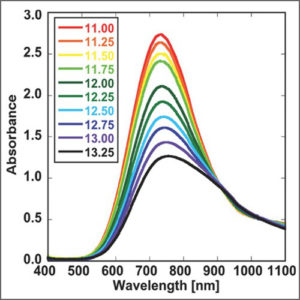
UV-Vis-NIR Spectroscopy
UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopy is routinely used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of various analytes, such as transition metal ions, organic compounds, and biological macromolecules.
-
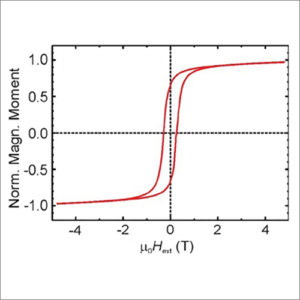
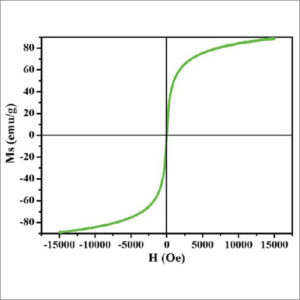
Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM)
Vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM) is a scientific instrument that measures magnetic properties of materials as a function of magnetic field.
-
Viscometer
Viscometer is used to measure the viscosity of a fluid, which includes rotational viscometer, glass capillary viscometer, etc.
-
Western Blot
Western blot is a laboratory method widely used to detect specific protein molecules from among a mixture of proteins.
-
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions.
-
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF)
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is an analytical technique that can be used to determine the chemical composition of a wide variety of sample types.
-
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
XPS can measure the elemental composition, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements at the surface of a material.
-
Zetasizer
Zetasizer is widely used to measure the particle size and zeta potential of colloids, particles, molecules and proteins in solution.