Chemical Analysis Methods
-
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Fluorescence spectroscopy measures the fluorescent light emitted from a sample at different wavelengths, after illumination with a xenon flash lamp.
-
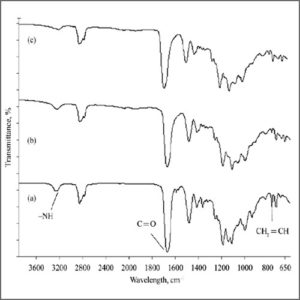
Fourier Transform Infrarred Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is an analytical technique used to identify organic (and in some cases inorganic) materials.
-
Karl Fischer Moisture Titration
Karl Fischer titration is an accurate method to determine trace amounts of water in a sample using uses coulometric or volumetric titration.
-
Kjeldahl Nitrogen Analyzer
Kjeldahl nitrogen analysis is to quantitatively determine the nitrogen contained in both organic substances and inorganic ammonia and ammonium.
-
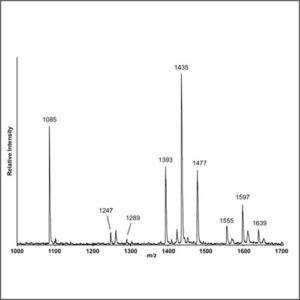
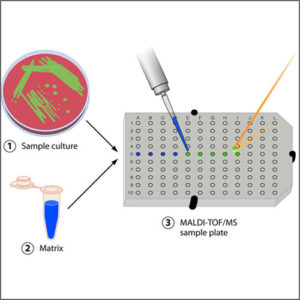
Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS)
Mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) is an analytical technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass to charge ratio.
-
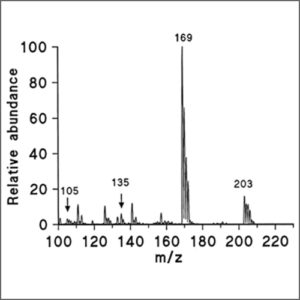
Mass Spectrometry (Q-TOF-MS)
Mass spectrometry (Q-TOF-MS) is an analytical technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass to charge ratio.
-
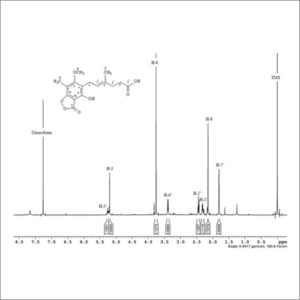
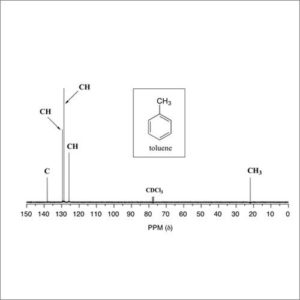
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
NMR spectroscopy is widely used to confirm the identity of a substance in organic chemistry and often highly predictable for small molecules.
-
Pyridine FTIR Spectroscopy
Pyridine FTIR is a useful method for the quantification ananlysis of the Bronsted and Lewis acidic sites at a catalyst surface.
-
UV-Vis-NIR Spectroscopy
UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopy is routinely used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of various analytes, such as transition metal ions, organic compounds, and biological macromolecules.
-
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions.
-
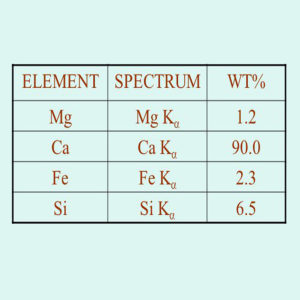
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF)
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is an analytical technique that can be used to determine the chemical composition of a wide variety of sample types.