Chromatography Analysis Methods
-
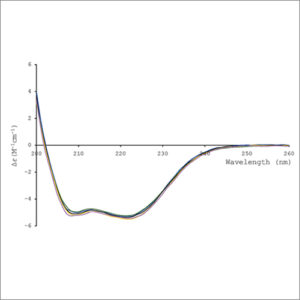
Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy (CD)
Circular dichroism spectroscopy (CD) uses circularly polarized light to investigate structural aspects of optically active chiral media.
-
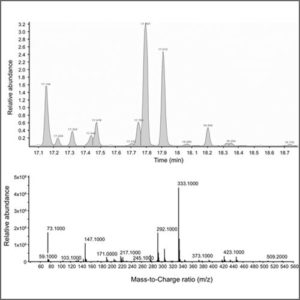
Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Gas chromatography – mass spectrometry (GC-MS) combines the features of gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample.
-
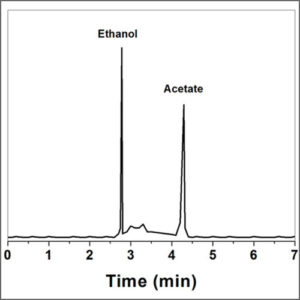
Gas Chromatography with FID/TCD/MS Detectors
Gas chromatography (GC) is used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition.
-
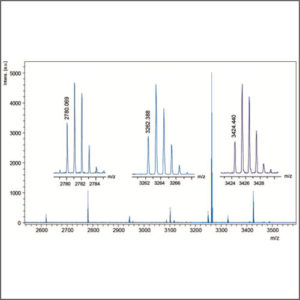
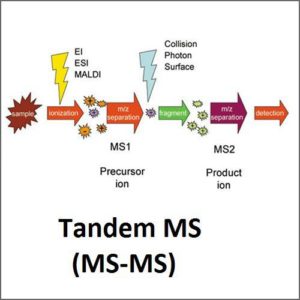
High Performance Liquid Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS)
High performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry.
-
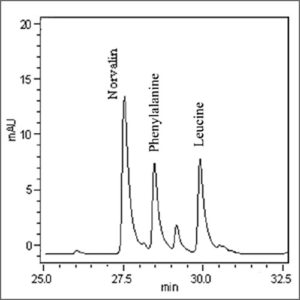
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture.
-
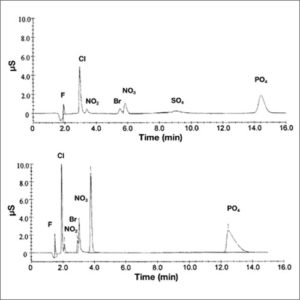
Ion Chromatography (IC)
Ion chromatography is a modified version of HPLC with a capacity for precise and highly sensitive detection of inorganic ions in a complex matrix.
-
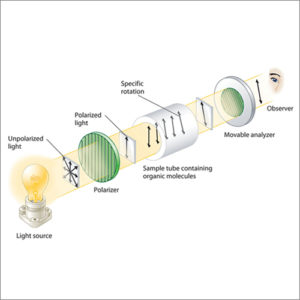
Polarimeter
Polarimetry measures the optical rotation angle of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid or solution.
-
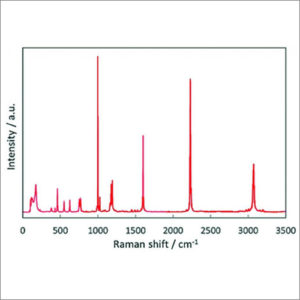
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique used to identify molecules and study chemical bonding and intramolecular bonds.
-
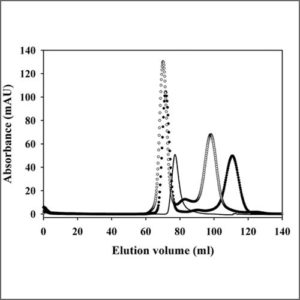
Size Exclusion Chromatography (GPC/GFC)
Size-exclusion chromatography is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size or by their molecular weight.