Surface Analysis Methods
-
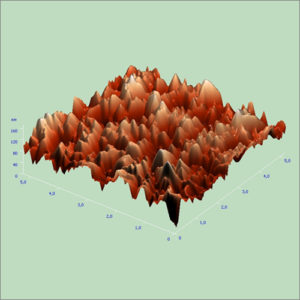
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a very high-resolution microscopy technology to study samples at atomic scale.
-
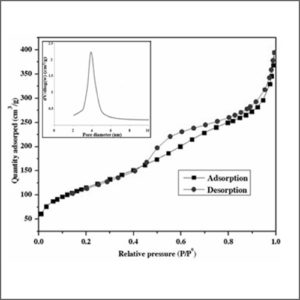
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller Analyzer (BET)
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller analyzer is the most common method for determining the surface area and pore size distribution of powders and porous materials.
-
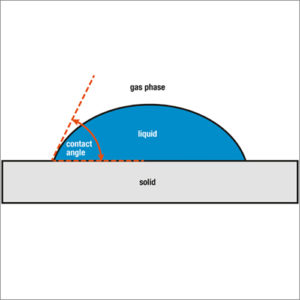
Contact Angle Analysis
Contact angle is an angle where a liquid-vapor interface meets a solid surface. It measures the wettability of a solid by a liquid.
-
Fluorescence Microscope
Fluorescence microscope uses fluorescence and phosphorescence to study properties of organic or inorganic substances.
-
Fourier Transform Infrarred Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is an analytical technique used to identify organic (and in some cases inorganic) materials.
-
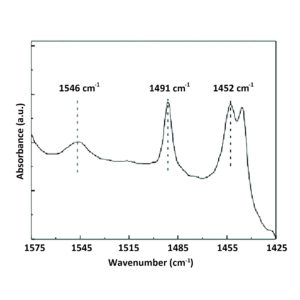
Pyridine FTIR Spectroscopy
Pyridine FTIR is a useful method for the quantification ananlysis of the Bronsted and Lewis acidic sites at a catalyst surface.
-
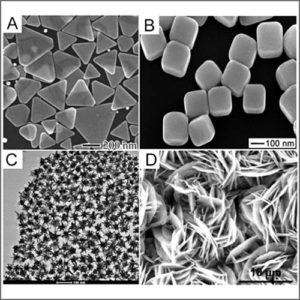
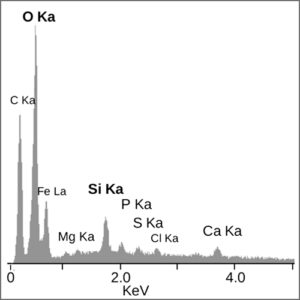
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM + EDX)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a non-destructive technique that uses an electron beam probe to analyse surface details down to nano-scale, and to produce high magnification images with high resolution.
-
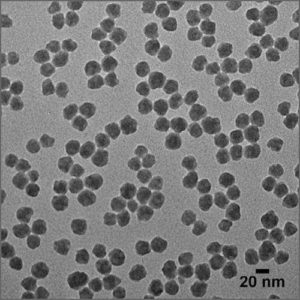
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Transmission electron microscope (TEM) utilizes energetic electrons to provide morphologic and size information on samples.
-
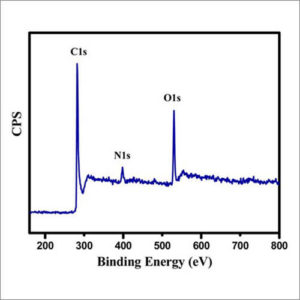
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
XPS can measure the elemental composition, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements at the surface of a material.