Microscopic Analysis Methods
-
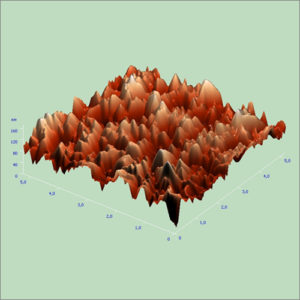
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a very high-resolution microscopy technology to study samples at atomic scale.
-
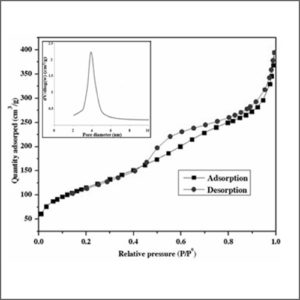
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller Analyzer (BET)
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller analyzer is the most common method for determining the surface area and pore size distribution of powders and porous materials.
-
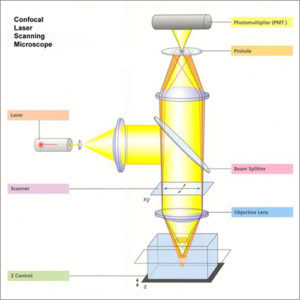
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) is an optical imaging technique to scan an object using a focused laser beam to allow for a 3-D reconstruction.
-
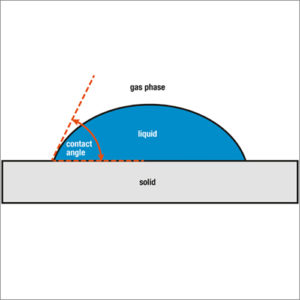
Contact Angle Analysis
Contact angle is an angle where a liquid-vapor interface meets a solid surface. It measures the wettability of a solid by a liquid.
-
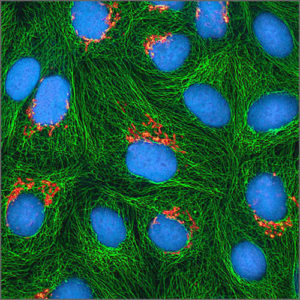
Fluorescence Microscope
Fluorescence microscope uses fluorescence and phosphorescence to study properties of organic or inorganic substances.
-
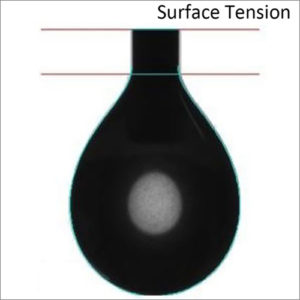
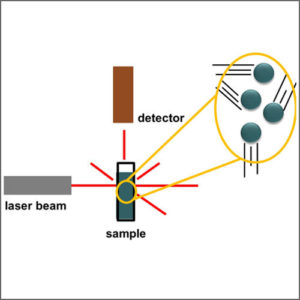
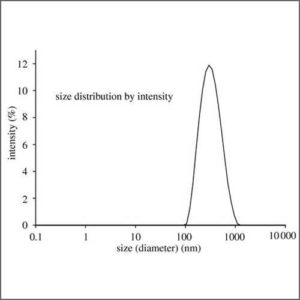
Laser Light Scattering (LLS)
Laser light scattering (LLS) is used to determine size of various particles including proteins, polymers, micelles and nanoparticles.
-
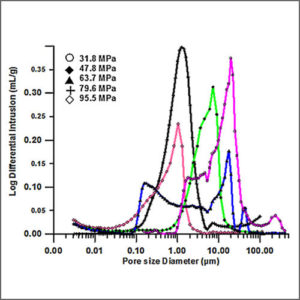
Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP)
Mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) is used to evaluate porosity, pore size distribution, and pore volume of various solid and powder materials.
-
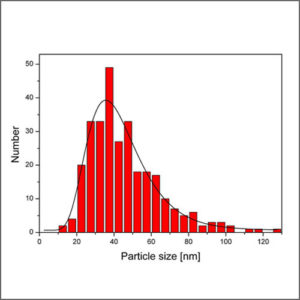
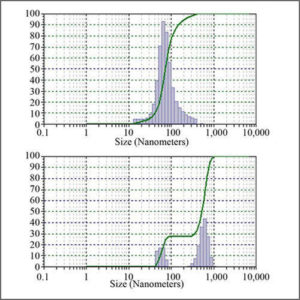
Particle Size Analyzer
Particle size analyzer provides accurate, reliable particle size distribution measurements from nanometers to millimetres.
-
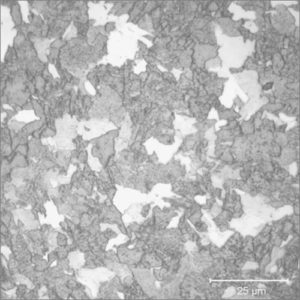
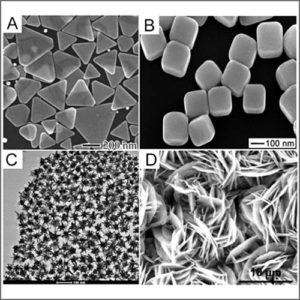
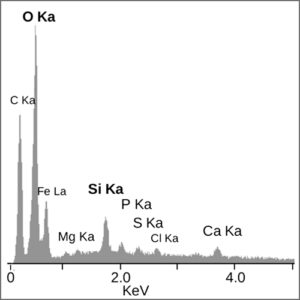
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM + EDX)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a non-destructive technique that uses an electron beam probe to analyse surface details down to nano-scale, and to produce high magnification images with high resolution.
-
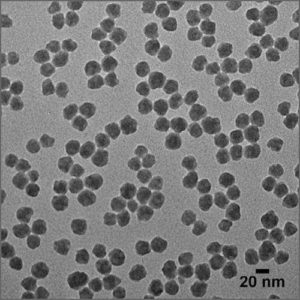
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Transmission electron microscope (TEM) utilizes energetic electrons to provide morphologic and size information on samples.
-
Zetasizer
Zetasizer is widely used to measure the particle size and zeta potential of colloids, particles, molecules and proteins in solution.