Optical Density Measurement (OD600)
Optical density measurement (OD or OD600) is used in microbiology to estimate the concentration of bacteria or other cells in a liquid.
- Description
| Testing Method | Optical Density Measurement (OD600) |
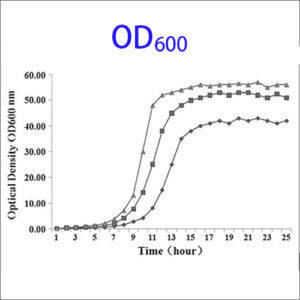
| Description | Optical density measurement (OD or OD600) is a common technology in microbiology to estimate the concentration of bacteria or other cells in a liquid. OD measurement is performed under the assumption that the OD value obtained is proportional to the concentration of bacterial in the liquid culture.
The light at the wavelength of 600nm is in the middle of the visible wavelength, easy to produce and does little to damage or hinder microbial growth. The optical density (OD) of a sample at 600nm is referred to as OD600. This is done by measuring the absorbance of the OD600 light with the use of a spectrophotometer. OD600 value gives an estimate of the concentration of the cells in the liquid, which can be used to estimate the growth phase of the population. The basic idea is to compare a sample of plain media, and a sample of media in which bacteria has been growing. Initially the levels of bacteria will be very low, and the amount of light absorbed by the two samples will be similar. The two samples are then placed in an incubator, and over time as the number of bacteria grow, this relative value will change according to the growth phase of the bacteria. At the beginning the OD600 measures close to zero, because the bacterial population in is the early lag growth phase, and there are few bacteria in total. Reproduction accelerates, and the bacteria are at their most reproductive period during the log or exponential phase. Beyond these phases, the bacterial population will stabilize and then decline. |
| More Information | Wikipedia: OD600 |