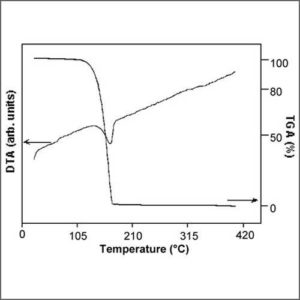
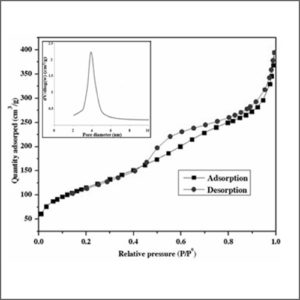
High Performance Liquid Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS)
High performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry.
- Description
| Testing Method | High Performance Liquid Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS);
High Performance Liquid Chromatography – Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS-MS) |
| Description | High performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS, or alternatively LC-MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of high Performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry (MS). HPLC-MS is a powerful technique that has very high sensitivity, making it useful in many applications. Its application is oriented towards the separation, general detection and potential identification of chemicals of particular masses in the presence of other chemicals (i.e., in complex mixtures), e.g., natural products from natural-products extracts, and pure substances from mixtures of chemical intermediates. Preparative HPLC-MS systems can be used for rapid mass-directed purification of specific substances from such mixtures that are important in basic research and pharmaceutical, agrochemical, food, and other industries.
HPLC-MS is very commonly used in pharmacokinetic studies of pharmaceuticals and is thus the most frequently used technique in the field of bio-analysis. These studies give information about how quickly a drug will be cleared from the hepatic blood flow, and organs of the body. MS is used for this due to high sensitivity and exceptional specificity compared to UV (as long as the analyte can be suitably ionised), and short analysis time.
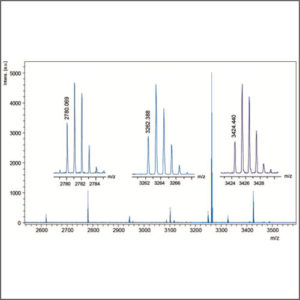
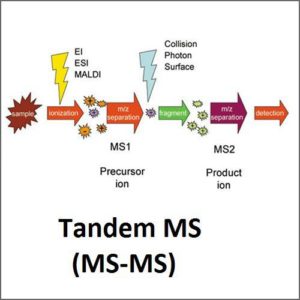
The major advantage MS has is the use of tandem MS-MS. The detector may be programmed to select certain ions to fragment. The process is essentially a selection technique, but is in fact more complex. The measured quantity is the sum of molecule fragments chosen by the operator. As long as there are no interferences or ion suppression, the LC separation can be quite quick.
HPLC-MS is also used in proteomics where again components of a complex mixture must be detected and identified in some manner. The bottom-up proteomics HPLC-MS approach to proteomics generally involves protease digestion and denaturation (usually trypsin as a protease, urea to denature tertiary structure and iodoacetamide to cap cysteine residues) followed by HPLC-MS with peptide mass fingerprinting or HPLC-MS-MS (Tandem MS) to derive sequence of individual peptides. HPLC-MS-MS is most commonly used for proteomic analysis of complex samples where peptide masses may overlap even with a high-resolution mass spectrometer. Samples of complex biological fluids like human serum may be run in a modern HPLC-MS-MS system and result in over 1000 proteins being identified, provided that the sample was first separated on an SDS-PAGE gel or HPLC-SCX.
HPLC-MS is frequently used in drug development at many different stages including peptide mapping, glycoprotein mapping, natural products dereplication, bioaffinity screening, in vivo drug screening, metabolic stability screening, metabolite identification, impurity identification, quantitative bioanalysis, and quality control. |
| More Information | Wikipedia: Liquid Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry ; Tandem mass spectrometry (MS-MS) |